Representational pattern similarity of electrical brain activity reveals rapid and specific prediction during language comprehension
Abstract
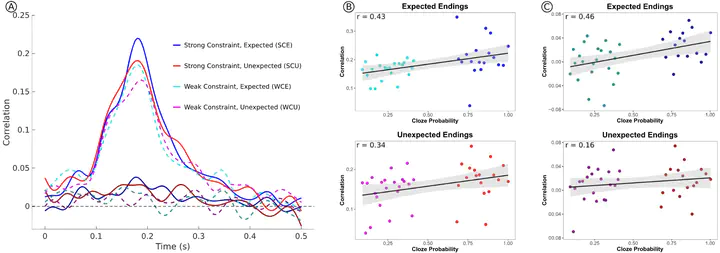
Predicting upcoming events is a critical function of the brain, and language provides a fertile testing ground for studying prediction, as comprehenders use context to predict features of upcoming words. Many aspects of the mechanisms of prediction remain elusive, partly due to a lack of methodological tools to probe prediction formation in the moment. To elucidate what features are neurally preactivated and when, we used representational similarity analysis on previously collected sentence reading data. We compared EEG activity patterns elicited by expected and unexpected sentence final words to patterns from the preceding words of the sentence, in both strongly and weakly constraining sentences. Pattern similarity with the final word was increased in an early time window following the presentation of the pre-final word, and this increase was modulated by both expectancy and constraint. This was not seen at earlier words, suggesting that predictions were precisely timed. Additionally, pre-final word activity—the predicted representation—had negative similarity with later final word activity, but only for strongly expected words. These findings shed light on the mechanisms of prediction in the brain: rapid preactivation occurs following certain cues, but the predicted features may receive reduced processing upon confirmation.