Abstract
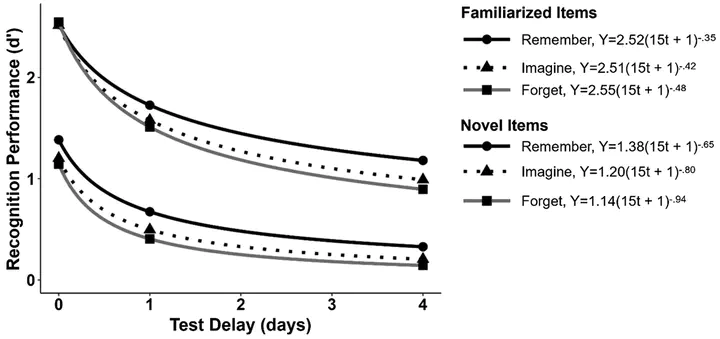
Across two experiments, we assessed the rates of relative forgetting following instructions to remember or forget information in an item-method directed forgetting paradigm across several retention intervals. In addition to the Forget and Remember cues, we also included Thought Substitution (TS) cues in the same design instructing participants to mentally shift to a different context on some study trials. TS cues have been shown to impair memory compared with Remember cues, but not as effectively as cues to Forget in item-method studies (Hubbard & Sahakyan, 2021). The results demonstrated that Forget cues produce accelerated rates of forgetting compared with Remember cues and showed that these differences are independent of initial learning rates, which were deliberately equated in Experiment 2. TS cued items showed faster forgetting than Remember cued items but were less effective than Forget cues and exhibited a more complex pattern likely reflecting individual differences. Thus, delayed testing demonstrated that active forgetting can have long-lasting effects on memory traces beyond initial suppression, in line with cognitive neuroscientific theory suggesting inhibition can produce lasting changes to memory traces.