The Impact of Linguistic Prediction Violations on Downstream Recognition Memory and Sentence Recall
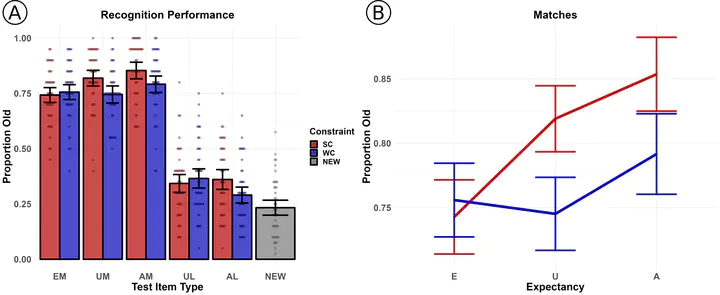
Abstract
Predicting upcoming words during language comprehension not only affects processing in the moment but also has consequences for memory, although the source of these memory effects (e.g., whether driven by lingering pre-activations, re-analysis following prediction violations, or other mechanisms) remains underspecified. Here, we investigated downstream impacts of prediction on memory in two experiments. First, we recorded EEG as participants read strongly and weakly constraining sentences with expected, unexpected but plausible, or semantically anomalous endings (“He made a holster for his gun / father / train”) and were tested on their recognition memory for the sentence endings. Participants showed similar rates of false alarms for predicted but never presented sentence endings whether the prediction violation was plausible or anomalous, suggesting that these arise from pre-activation of the expected words during reading. During sentence reading, especially in strongly constraining sentences, plausible prediction violations elicited an anterior positivity; anomalous endings instead elicited a posterior positivity, whose amplitude was predictive of later memory for those anomalous words. ERP patterns at the time of recognition differentiated plausible and anomalous sentence endings: Words that had been plausible prediction violations elicited enhanced late positive complex amplitudes, suggesting greater episodic recollection, whereas anomalous sentence endings elicited greater N1 amplitudes, suggesting attentional tagging. In a follow-up behavioral study, a separate group of participants read the same sentence stimuli and were tested for sentence-level recall. We found that recall of full sentences was impaired when sentences ended with a prediction violation. Taken together, the results suggest that prediction violations draw attention and affect encoding of the violating word, in a manner that depends on plausibility, and that this, in turn, may impair future memory of the gist of the sentence.